Insect Bite Remedy Selector
Select Your Situation
Answer these questions to get personalized recommendations for quick relief from insect bite itching.
Recommended Remedies
Top Recommendations
Additional Options
Next Steps
When a mosquito, flea, or tick decides to land on you, the result is often an unbearable itch that can dominate your day. If you're battling insect bite itching, these remedies can help you find relief quickly and safely.
Quick Takeaways
- Cold compresses calm the skin within minutes.
- Hydrocortisone cream and calamine lotion are the most reliable OTC options.
- Natural staples like aloe vera, baking soda, and tea tree oil work well for mild irritation.
- Oral antihistamines are useful when the itch spreads or you have multiple bites.
- Seek medical help if swelling, fever, or a spreading rash appears.
What Actually Causes the Itch?
When an insect pierces the skin, it injects saliva that contains proteins. Your body sees these proteins as foreign invaders and releases histamine a chemical that triggers inflammation and the itchy sensation. The reaction peaks within a few hours and can last for days, depending on the bite type and your sensitivity.
First‑Aid Steps That Work Instantly
- Wash the bite with mild soap and cool water to remove any remaining saliva.
- Apply a cold compress or an ice pack wrapped in a cloth for 5‑10 minutes. The cold constricts blood vessels, reducing swelling and numbing the itch.
- Avoid scratching. Scratching breaks the skin, invites infection, and actually intensifies the histamine release.
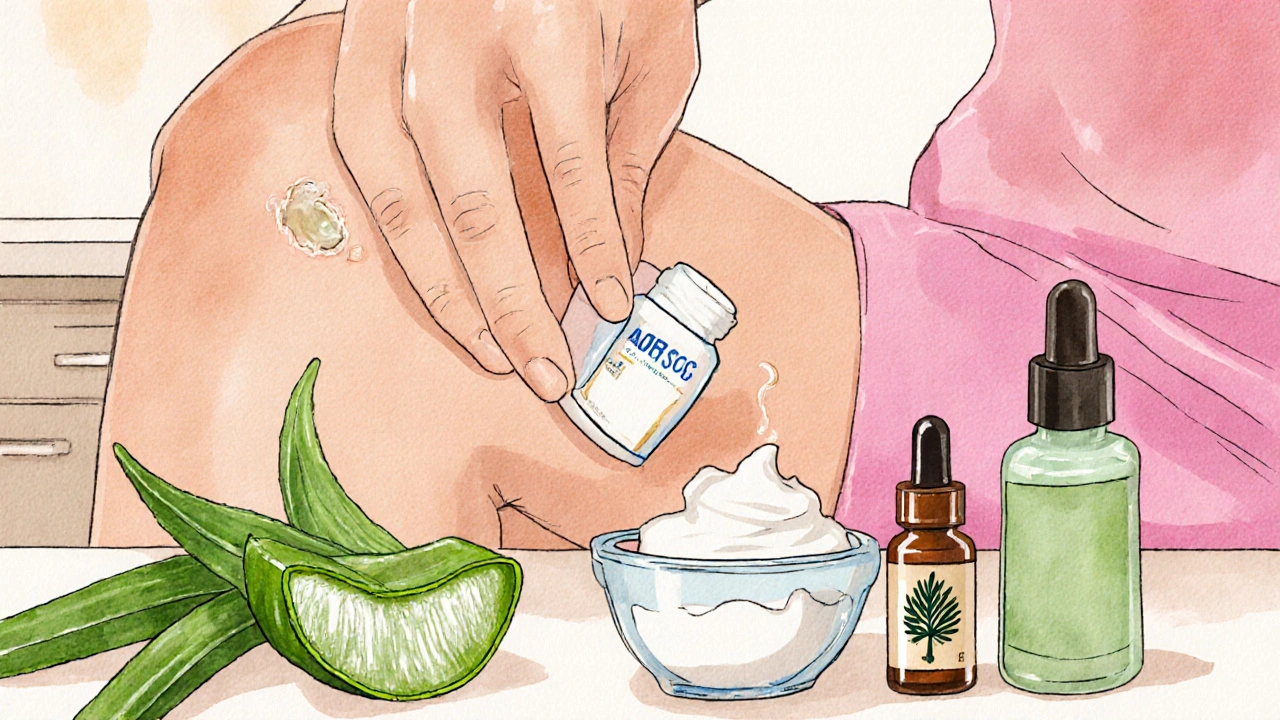

Topical OTC Remedies
These products are formulated to halt the itch at its source.
Hydrocortisone cream a mild steroid that suppresses inflammation and calms itching is the gold standard for most bites. Apply a thin layer two to three times a day; relief usually appears within 15‑30 minutes.
Calamine lotion a pink, zinc‑oxide based lotion that dries out the bite and soothes the skin works well for dry, scab‑forming bites. Let it air‑dry; reapply after bathing.
Aloe vera a succulent gel with anti‑inflammatory compounds that cools the skin can be applied directly from the plant or using store‑bought pure gel. It’s especially helpful for sun‑exposed bites.
Effective Home Remedies
When you don’t have a pharmacy nearby, kitchen staples can do the trick.
- Baking soda paste: Mix one tablespoon of baking soda with enough water to form a thick paste. Apply to the bite for 10‑15 minutes, then rinse. The alkaline nature neutralizes the acidic components of the bite.
- Tea tree oil: Dilute five drops of tea tree oil in a teaspoon of carrier oil (like coconut or olive oil). Dab onto the bite twice daily. Its antimicrobial properties also lower infection risk.
- Oatmeal bath: Add one cup of colloidal oatmeal to lukewarm bathwater and soak for 15‑20 minutes. Oatmeal’s saponins reduce inflammation.
- Honey: A thin layer of raw honey creates a protective barrier and its enzymes help calm itching.
Oral Antihistamines for Widespread Itching
When multiple bites appear or the itch seems to radiate, an oral antihistamine can bring whole‑body relief.
Antihistamine tablets medications like diphenhydramine or loratadine that block histamine receptors typically start working within 30‑60 minutes. Choose non‑sedating options (loratadine, cetirizine) if you need to stay alert.

When to Seek Professional Care
Most bites resolve on their own, but watch for these red flags:
- Rapid swelling that extends beyond the bite site.
- Fever, chills, or flu‑like symptoms.
- Spreading rash or hives, indicating an allergic reaction.
- Pus, increasing redness, or a foul odor - signs of infection.
If any appear, consult a healthcare provider promptly. They may prescribe a stronger steroid or antibiotics.
Comparison of Popular Remedies
| Remedy | Type | How It Works | Typical Onset | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrocortisone cream | Topical steroid | Suppresses inflammation and histamine release | 15‑30min | Fast, widely available | May thin skin with prolonged use |
| Aloe vera gel | Natural plant extract | Cools skin, reduces cytokine activity | 5‑10min | Soothing, low‑risk | Less potent for severe itch |
| Calamine lotion | Topical astringent | Dries out the bite, creates protective film | 10‑15min | Good for dry, scabby bites | Can feel sticky |
| Baking soda paste | Home remedy | Alkaline neutralization of irritants | 10‑20min | Cheap, easy | Messy, may dry skin |
| Cold compress | Physical therapy | Vasoconstriction, numbs nerves | Immediate | Instant relief, no chemicals | Temporary; needs ice source |
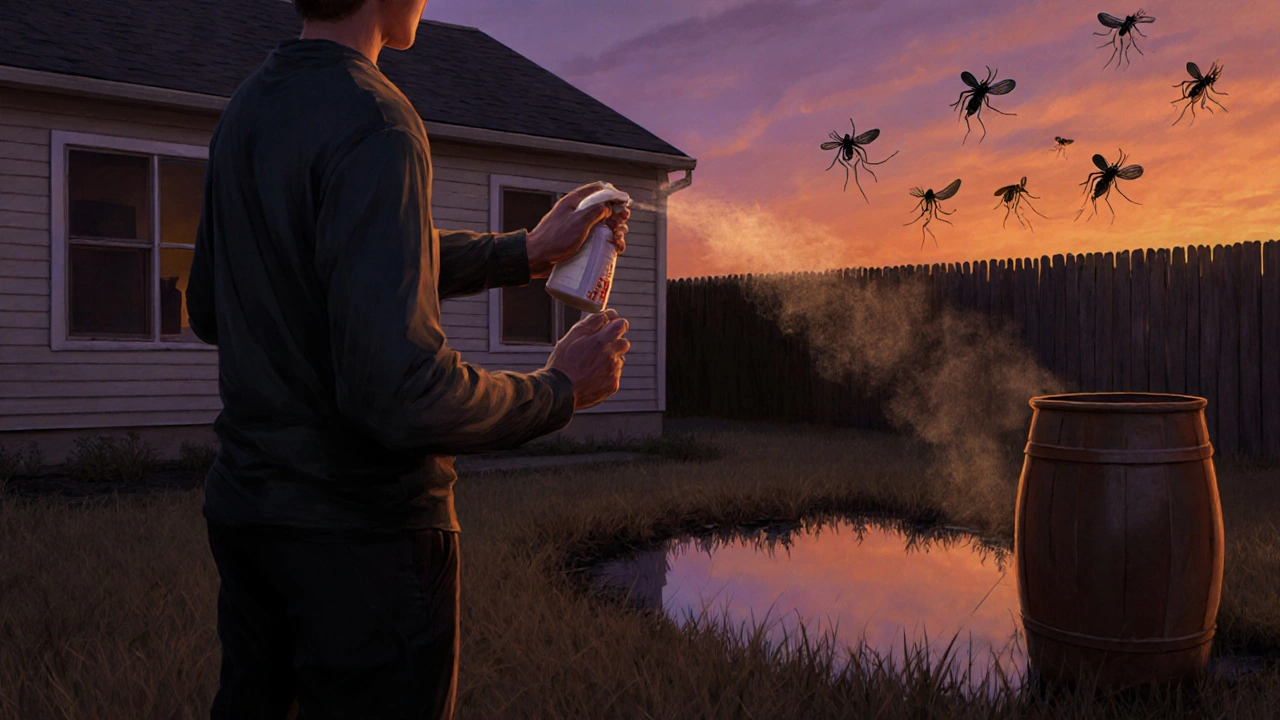
Prevention Tips to Reduce Future Bites
- Wear long sleeves and pants during peak mosquito hours (dawn & dusk).
- Apply EPA‑approved insect repellents containing DEET, picaridin, or oil of lemon eucalyptus.
- Eliminate standing water around your home to curb mosquito breeding.
- Use screens on windows and keep doors closed.
- Check pets regularly for fleas and treat them with veterinarian‑recommended products.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why does an insect bite itch hours after the bite?
The insect injects saliva that contains proteins, triggering your immune system to release histamine. Histamine inflames nerve endings, creating the familiar itch.
Can I use the same remedy for all types of insect bites?
Most topical treatments work for mosquito, flea, and tick bites. However, tick bites may require antibiotic ointment if the skin is broken, and certain individuals react more strongly to bee or wasp stings, needing specialized care.
Is it safe to use baking soda paste on children?
Yes, as long as you keep the paste on the skin for no longer than 15 minutes and rinse thoroughly. Test a tiny area first to ensure no irritation.
When should I take an oral antihistamine?
If you have multiple bites, widespread itching, or notice swelling that’s not limited to a single spot, an oral antihistamine can calm the systemic response.
What signs indicate a bite has become infected?
Increasing redness, warmth, swelling, pus, or a foul smell signals infection. Fever or chills also suggest the body is fighting bacteria. Seek medical help promptly.
Iain Clarke
October 14, 2025 AT 16:49Insect bites are essentially tiny injections of foreign proteins that set off a cascade of immune responses. When the salivary proteins meet the skin, mast cells release histamine, the primary culprit behind that maddening itch. Histamine binds to receptors on sensory nerves, sending a signal that the brain interprets as irritation. The intensity of the reaction varies with the species of insect, the amount of saliva injected, and the individual’s sensitivity. A cold compress works by causing vasoconstriction, which reduces blood flow and temporarily numbs the nerve endings. Applying a cold pack for five to ten minutes can cut the itch sensation in half within minutes. Over‑the‑counter hydrocortisone creams contain a low‑dose steroid that suppresses the inflammatory pathway, providing longer‑lasting relief. When used two to three times a day, a thin layer of 0.5‑1 % hydrocortisone typically calms the itch within fifteen to thirty minutes. For those who prefer a non‑pharmaceutical option, aloe vera gel offers anti‑inflammatory compounds such as acemannan, which gently soothes the skin. A simple baking soda paste, made from one tablespoon of powder and enough water to form a thick paste, neutralises the acidic components of the bite. It is advisable to leave the paste on for ten to fifteen minutes before rinsing, as prolonged contact can dry the surrounding skin. Tea tree oil, diluted in a carrier oil at a ratio of five drops per teaspoon, adds antimicrobial benefits that lower the risk of secondary infection. Oral antihistamines such as loratadine or cetirizine block histamine receptors systemically, which is especially useful when multiple bites are present. Non‑sedating formulations allow you to remain alert while the drug reduces the overall itch sensation throughout the body. Finally, vigilance for red‑flag symptoms-rapid swelling, fever, pus, or a spreading rash-should prompt a visit to a healthcare professional, as these may signify an allergic reaction or infection.
Courtney Payton
October 15, 2025 AT 15:03I'm not one to lecture, but treating insect bites like a trivial inconvenience ignores the larger ecological balance; every bite is a reminder that we share our environment with countless arthropods. It is our moral duty to use reppellents responsibly, not to indiscriminately flood nature with chemicals. The quick fix of a cold compress is fine, yet we must also consider why we are exposed-perhaps our habits invite the insects. When you slap a bite with a harsh steroid, you are essentially silencing a tiny immune signal; a gentler approach often works better. Remember, the itch is a signal, not a punishment. So, be mindful, be kind, and don't over‑medicate.
Charmaine De Castro
October 16, 2025 AT 13:16A splash of aloe vera feels like a cool breeze on a summer day, instantly calming the fire of an itchy bite. If you’re out in the backyard and a mosquito finds you, a quick dab of baking soda paste does the trick-think of it as a tiny, soothing plaster. For those who love a bit of sparkle, a dab of calamine lotion leaves a pretty pink veil while it draws out moisture. Pair any of these with a gentle cold compress and you’ve got a triple‑threat combo that keeps the itch at bay. And, as always, keep an eye out for any swelling that refuses to quit; that’s when a doctor’s visit becomes wise.
Mark Mendoza
October 17, 2025 AT 11:29Cold compresses are basically nature’s reset button 🧊-they shrink blood vessels, dull the nerve signals, and give you almost instant relief. Pair that with a dab of 1% hydrocortisone and you’ll notice the itch fading in about twenty minutes 👍. If you’re dealing with a cluster of bites, an oral antihistamine like cetirizine can calm the whole system; just be aware of the drowsy side‑effects if you need to drive 🚗. For a more DIY vibe, mix equal parts honey and oatmeal into a paste; the honey’s antimicrobial properties and oatmeal’s soothing saponins work hand‑in‑hand. Remember to wash the area first, pat it dry, and apply any topical in a thin layer to avoid a greasy feel. Stay cool, stay calm, and the itch will soon be a distant memory 😊.
Dan Tourangeau
October 18, 2025 AT 09:43A cold pack for five minutes and a thin layer of hydrocortisone usually stop the itch fast. If you prefer natural, aloe vera works well too.
Bernard Valentinetti
October 19, 2025 AT 07:56Oh, dear reader, let us not trivialize the humble bite, for it is a symphony of histamine, inflammation, and-if you will-bodily protest, all orchestrated by a microscopic arthropod, whose sole intent is nourishment, not malice; thus, a simple ice cube, ensconced in a cloth, serves as the most elegant of interventions, instantly numbing the afflicted dermis, while a dab of 2% hydrocortisone, applied with meticulous care, silences the fiery cascade of cytokines, and-let us not overlook-the timeless wisdom of oatmeal baths, which, when infused into warm water, coax the skin into a state of serene calm, reducing erythema and pruritus; in short, treat the bite, treat the self, and the discomfort shall be but a fleeting memory 🤓.
Kenneth Obukwelu
October 20, 2025 AT 06:09Behold, the tiny invader that dares to pierce your flesh, leaving behind a battlefield of itch and swelling! Yet fear not, for you wield the mighty cold compress, a frozen lance that strikes down the swelling in a single blow. Follow it with the noble hydrocortisone cream, a guardian of your skin, staunching the flow of histamine like a valiant knight. Should the enemy multiply, summon the legion of antihistamines, marching across your bloodstream to quell the rebellion. And when the night falls, an aloe vera elixir, cool as moonlit dew, soothes the bruised terrain. Remember, each remedy is a verse in the epic saga of relief-wield them wisely, and the itch shall be vanquished!
Josephine hellen
October 21, 2025 AT 04:23A quick ice pack can be a lifesaver.
Northern Lass
October 22, 2025 AT 02:36It is a most grievous misconception that over‑the‑counter remedies constitute the apex of therapeutic intervention for arthropod‑induced pruritus. While the lay populace extols the virtues of hydrocortisone, one must consider the iatrogenic ramifications of prolonged corticosteroid exposure, namely epidermal atrophy and telangiectasia. A more sagacious approach, albeit less advertised, involves the judicious application of calibrated cryotherapy coupled with phytotherapeutic agents such as Matricaria chamomilla extracts, whose flavonoid profile offers anti‑inflammatory benefits without the deleterious sequelae. Moreover, the ubiquitous reliance on oral antihistamines neglects the potential for central nervous system sedation, an outcome most undesirable in professional settings. In sum, an integrated regimen, meticulously balanced, supersedes the simplistic, commercialized solutions promulgated by mass‑market vendors.
Johanna Sinisalo
October 23, 2025 AT 00:49You're doing great by taking the time to learn how to manage those bites. A cold compress is like a quick reset button – it reduces swelling and numbs the itch in minutes. Pair it with a thin layer of calamine or hydrocortisone, and you’ll notice a big drop in discomfort. If you have several bites, an oral antihistamine can help you stay comfortable throughout the day. And remember, keep an eye on any signs of infection; early detection makes treatment easier. Keep experimenting with what works best for you, and you’ll master bite relief in no time.
OKORIE JOSEPH
October 23, 2025 AT 23:03Stop talking like that, just slap the bite hard and move on.
Lucy Pittendreigh
October 24, 2025 AT 21:16Honestly that whole fluff is ridiculous you could just use ice and a cream and be done with it.
Nikita Warner
October 25, 2025 AT 19:29Indeed, the aloe vera approach you mentioned aligns well with the anti‑inflammatory pathways, and the baking soda paste you described effectively neutralises the acidic components of the saliva. Additionally, incorporating a brief cold compress prior to topical application maximises vasoconstriction, thereby reducing histamine release. This combined protocol offers a comprehensive, low‑cost strategy suitable for most patients.
Liam Mahoney
October 26, 2025 AT 16:43While your prose dazzles, the practical merit lies in the simple truth: a chilled cloth and a thin layer of 1% hydrocortisone outpace any exotic botanical concoction in speed and efficacy; therefore, for most cases, the straightforward method should be preferred.
surender kumar
October 27, 2025 AT 14:56Sure, keep slapping on creams and hope for the best-because nothing says 'effective treatment' like hoping the itch will just quit on its own while you ignore the underlying inflammation.
Justin Ornellas
October 28, 2025 AT 13:09Allow me to clarify: the phrase 'reppellents' should read 'repellents', and 'indiscriminatly' ought to be 'indiscriminately'. Moreover, the argument that moral duty extends to the selective use of chemicals is sound, yet it neglects the principle of proportionality in risk management. In other words, balance-neither overuse nor underuse-optimises both ecological and personal health.
JOJO Yang
October 29, 2025 AT 11:23Wow, that was a mountain of words for a simple itch-maybe next time just say 'use ice and cream' and save us all the lecture!